Speak with a Sydney commercial lawyer: (02) 8806 0866 · Commercial Law — Jameson Law · What is Commercial Law? · Commercial Disputes · Official resources: Federal Register of Legislation · ACCC (ACL) · IP Australia · Fair Work
Commercial law forms the backbone of business operations, governing everything from contracts to intellectual property. At Jameson Law, we often encounter clients seeking to define commercial law and understand its key components.
This blog post will break down the essential areas of commercial law, explain crucial definitions, and highlight common disputes that businesses may face. By the end, you’ll have a clearer grasp of commercial law’s significance in the business world.
Key Areas of Commercial Law
Commercial law encompasses several critical domains that shape business operations and relationships. Understanding these areas can significantly impact a company’s success.
Contract Law: The Foundation of Business Relationships
Contract law forms the cornerstone of commercial transactions. It governs agreements between parties, setting out rights, obligations, and remedies. In Australia, the Contract Law Act 1969 (WA) provides a framework for contract formation and enforcement.
A well-drafted contract can save businesses thousands in potential disputes. For example, a clear force majeure clause could have protected many Australian companies during the COVID-19 pandemic. Professional contract drafting and review can help avoid costly misunderstandings.
Corporate Governance: Steering Your Business Right
Corporate governance involves the systems and processes by which companies are directed and controlled. The Corporations Act 2001 (Cth) sets out the legal framework for corporate governance in Australia.
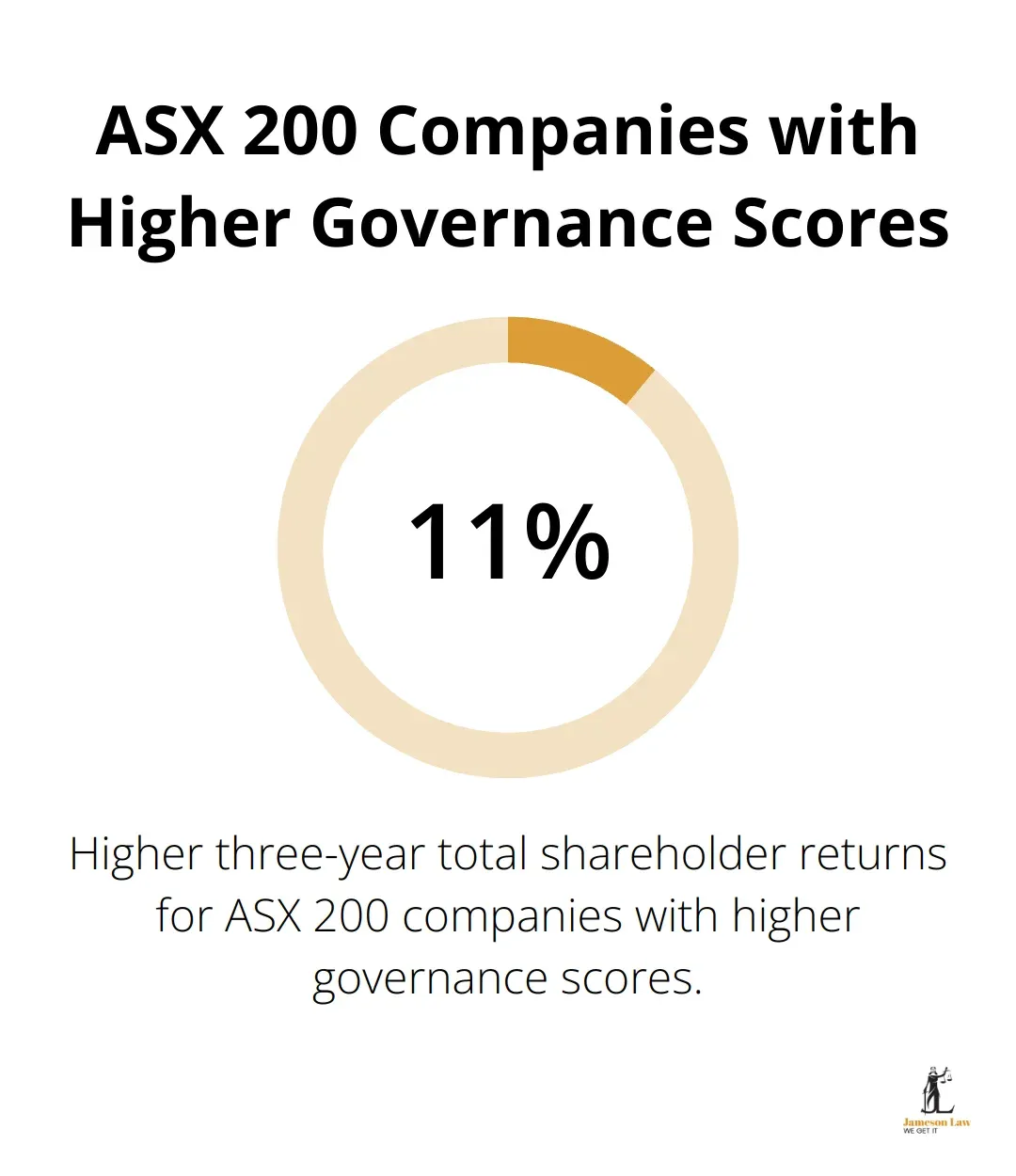
Good governance isn’t just about compliance; it creates value. Companies with strong governance practices often outperform their peers. A 2020 study by KPMG Australia found that ASX 200 companies with higher governance scores achieved 11% higher three-year total shareholder returns.
Intellectual Property: Protecting Your Business Assets
Intellectual property (IP) law safeguards creations of the mind, such as inventions, designs, and brands. In Australia, IP Australia administers these rights.
The value of IP cannot be overstated. According to IP Australia, intangible assets (including IP) account for more than 90% of the value of companies in the S&P 500. Early registration of trade marks and patents can prevent costly legal battles down the line.
Employment Law: Managing Your Most Valuable Resource
Employment law regulates the relationship between employers and employees. The Fair Work Act 2009 (Cth) is the primary legislation governing workplace relations in Australia.
Compliance with employment law is essential. Regular audits of employment practices can help businesses avoid hefty fines and reputational damage.
Consumer Protection: Building Trust and Compliance
Consumer protection laws ensure fair trading practices and protect consumers from unfair business conduct. The Australian Consumer Law (ACL) is the main legislation in this area.
Violations of consumer law can be costly. Robust compliance programmes can help businesses mitigate these risks.
Understanding these key areas of commercial law is essential for any business operating in Australia. Professional legal advice can help navigate these complex legal landscapes, ensuring compliance and fostering growth. Now, let’s explore some important commercial law definitions that every business owner should know.
Key Commercial Law Terms Explained
Commercial law contains complex terminology that business owners must understand to make informed decisions and protect their interests. This chapter breaks down five essential commercial law definitions every business owner should know.
Breach of Contract: When Agreements Unravel
A breach of contract happens when one party fails to fulfil their obligations outlined in a legally binding agreement. This can range from minor infractions to material breaches that undermine the contract’s purpose. In Australia, legal remedies for contract breaches may include damages, specific performance, contract termination, and injunctions.
To protect your business, ensure contracts are clear, specific, and include dispute resolution provisions. Regular contract audits can identify potential issues before they escalate into costly legal battles.
Fiduciary Duty: The Trust Obligation
Fiduciary duty is a legal obligation to act in the best interests of another party. This concept is particularly relevant in corporate governance, where directors and officers have a fiduciary duty to their company and shareholders.
The overriding duty of a fiduciary is the obligation of undivided loyalty. This obliges the director to act honestly, in good faith and to the best of their abilities in the interests of the company.
To uphold fiduciary duties, business leaders should maintain transparency in decision-making processes, avoid conflicts of interest, and regularly review corporate governance policies.
Intellectual Property Rights: Protecting Your Creations
Intellectual property (IP) rights include trade marks, copyrights, patents, and trade secrets. These legal protections are essential for businesses to maintain their competitive edge and monetise their innovations.
For businesses, early registration of IP rights can prevent costly disputes and protect valuable assets.
Unfair Dismissal: Employee Rights Protection
Unfair dismissal refers to the termination of employment in a harsh, unjust, or unreasonable manner.
To mitigate the risk of unfair dismissal claims, employers should establish clear performance expectations and disciplinary procedures, document all performance issues and conversations, and provide opportunities for improvement before considering termination.
Consumer Guarantees: Fair Trade Assurance
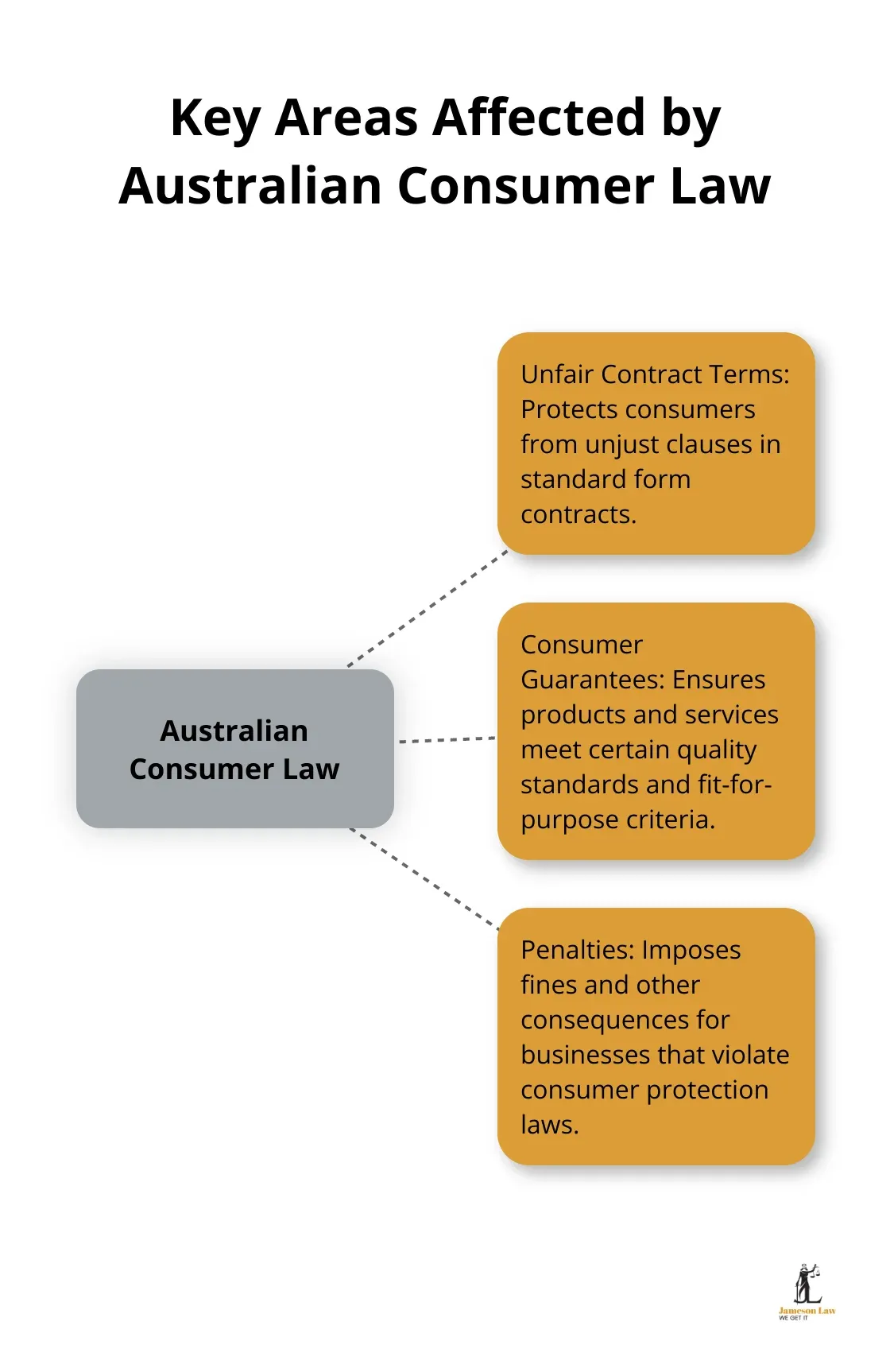
Consumer guarantees are automatic rights provided to consumers under the Australian Consumer Law. These guarantees ensure that products and services meet certain standards, are fit for purpose, and match any descriptions provided.
The Australian Consumer Law (ACL) directly affects business contracts in three key areas: Unfair Contract Terms, Consumer Guarantees, and Penalties. Businesses must understand and comply with these guarantees to avoid hefty fines and reputational damage.
Understanding these key commercial law terms is just the beginning. In the next chapter, we’ll explore common commercial law disputes that businesses often face and how to navigate them effectively.
Navigating Common Commercial Law Disputes
Commercial law disputes can significantly impact businesses, potentially leading to financial losses and reputational damage. We’ve observed how these conflicts disrupt operations and strain relationships. This chapter explores the most frequent commercial law disputes and provides practical strategies for prevention and resolution.
Contract Disputes: The Cornerstone of Commercial Conflicts
Commercial litigation trends are reshaping Australian business disputes. These often arise from misinterpretations, breaches, or disagreements over contract terms.
To minimise contract disputes:
 Use clear, unambiguous language in all agreements
Use clear, unambiguous language in all agreements Include detailed dispute resolution clauses
Include detailed dispute resolution clauses Review and update contracts regularly
Review and update contracts regularly Keep thorough records of all contract-related communications
Keep thorough records of all contract-related communications
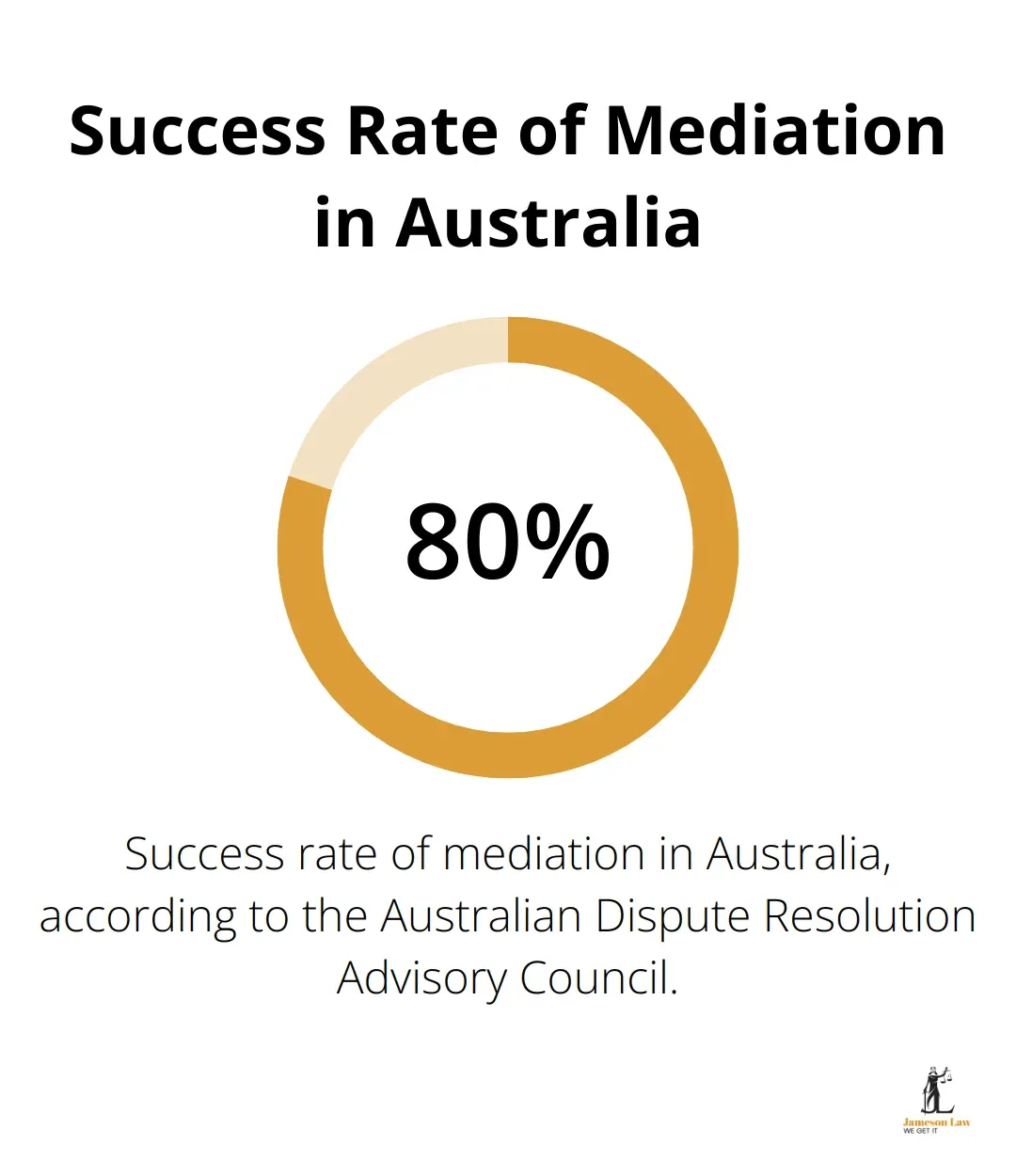
Consider alternative dispute resolution methods like mediation before litigation. A study by the Australian Dispute Resolution Advisory Council found that the success rate of mediation in Australia is around 80%.
Shareholder Conflicts: When Business Relationships Sour
Shareholder disputes can threaten a company’s existence. These conflicts often stem from disagreements over company direction, dividend payments, or alleged breaches of shareholder agreements.
To mitigate shareholder conflicts:
 Draft comprehensive shareholder agreements
Draft comprehensive shareholder agreements Implement clear decision-making processes
Implement clear decision-making processes Maintain open and regular communication among shareholders
Maintain open and regular communication among shareholders Consider including buy-sell provisions in shareholder agreements
Consider including buy-sell provisions in shareholder agreements
Early intervention is key in resolving shareholder disputes. Engaging a commercial law expert at the first sign of conflict can help prevent escalation and protect the company’s interests.
Intellectual Property Infringement: Protecting Your Business Assets
IP infringement cases continue to rise as businesses increasingly rely on intangible assets. Recent updates to trade mark law in Australia have refined the opposition process with clearer guidelines for evidence submission and decision.
To safeguard your intellectual property:
 Register all eligible IP rights promptly
Register all eligible IP rights promptly Conduct regular IP audits
Conduct regular IP audits Implement strong confidentiality agreements
Implement strong confidentiality agreements Monitor the market for potential infringements
Monitor the market for potential infringements
If you suspect IP infringement, act swiftly. Delay in enforcement can weaken your position and potentially lead to loss of rights. Seek legal advice to determine the best course of action, whether it’s sending a cease and desist letter or initiating legal proceedings.
Unfair Dismissal Claims: Navigating Employment Disputes
Unfair dismissal claims represent a significant portion of employment-related disputes.
To reduce the risk of unfair dismissal claims:
 Establish clear performance expectations and disciplinary procedures
Establish clear performance expectations and disciplinary procedures Document all performance issues and conversations
Document all performance issues and conversations Provide opportunities for improvement before considering termination
Provide opportunities for improvement before considering termination Ensure compliance with relevant awards and enterprise agreements
Ensure compliance with relevant awards and enterprise agreements
If faced with an unfair dismissal claim, seek immediate legal advice. Early intervention can often lead to quicker resolution and potentially avoid costly tribunal proceedings.
Consumer Law Violations: Maintaining Fair Trade Practices
Violations of consumer law can result in significant penalties and reputational damage.
To ensure compliance with consumer law:
 Implement a comprehensive compliance programme
Implement a comprehensive compliance programme Train staff regularly on consumer law obligations
Train staff regularly on consumer law obligations Review marketing materials and sales practices for potential misleading conduct
Review marketing materials and sales practices for potential misleading conduct Establish clear procedures for handling customer complaints and refunds
Establish clear procedures for handling customer complaints and refunds
If you receive a complaint or notice from a regulatory body, address it promptly and seek legal advice if necessary. Proactive engagement with regulators can often lead to more favourable outcomes.
Navigate commercial disputes law effectively with expert insights and strategies to resolve conflicts. Professional legal advice proves invaluable in navigating the complexities of commercial law in Australia.
Final Thoughts
Commercial law defines the legal framework for business operations in Australia. This complex field encompasses various areas, from contract law to consumer protection, each shaping business relationships and practices. A solid understanding of commercial law principles helps businesses navigate challenges, seize opportunities, and maintain compliance with legal obligations.
Professional legal advice proves invaluable in commercial matters. Commercial law constantly evolves, with new precedents and legislative changes reshaping the legal landscape. Expert counsel provides up-to-date insights, interprets complex legal jargon, and offers strategic advice tailored to specific situations (preventing disputes, protecting assets, and ensuring smooth business operations).
At Jameson Law, we assist businesses with a wide range of commercial law matters. Our team of experienced lawyers can help define commercial law concepts in practical terms, offering clear guidance on how these principles apply to your specific business context. We provide comprehensive support across various areas of commercial law, working closely with our clients to develop tailored strategies that support business growth and success. Call our Sydney office on (02) 8806 0866 or request a consultation.













