Australian commercial law is a complex field that governs business transactions and relationships. At Jameson Law, we understand the importance of providing a concise overview of this crucial area.
This blog post will explore key aspects of Australian commercial law, including contract law, corporate law, consumer protection, and intellectual property. We’ll also examine important legislation and dispute resolution methods that shape the commercial landscape in Australia.
Key Areas of Australian Commercial Law
Australian commercial law encompasses several critical domains that shape business operations and transactions. Understanding these key areas is essential for any business operating in Australia.
Contract Law: The Foundation of Business Relationships
Contract law forms the backbone of commercial interactions. In Australia, a valid contract requires offer, acceptance, consideration, and intention to create legal relations. The recent changes to unfair contract terms (UCT) laws have significantly impacted businesses. As of November 2023, the maximum penalties for including unfair terms in standard form contracts have increased to $50 million for companies.
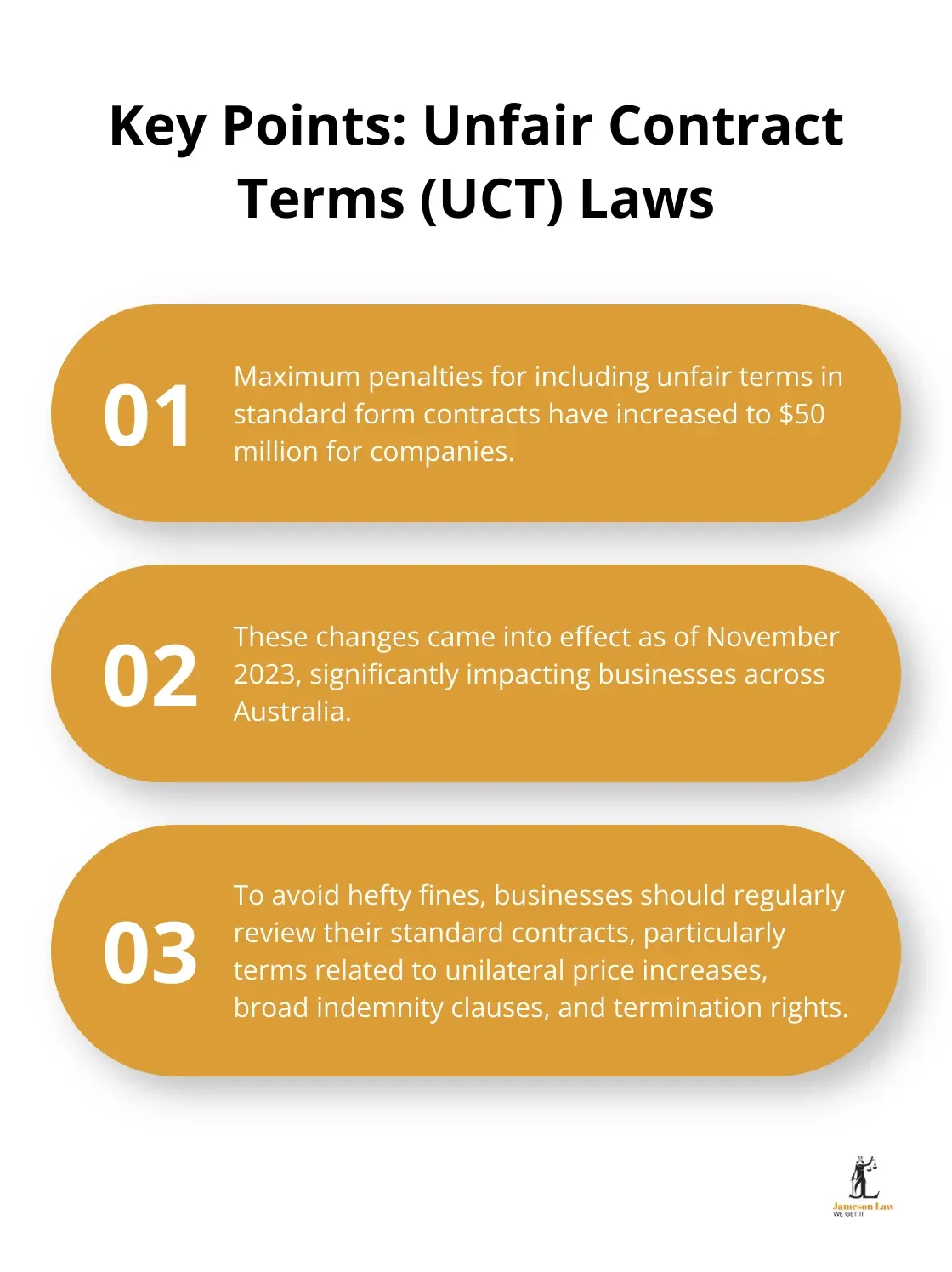
To avoid these hefty fines, businesses should review their standard contracts regularly. This is particularly important for terms related to unilateral price increases, broad indemnity clauses, and termination rights. Many cases have shown that seemingly innocuous clauses can lead to substantial legal issues.
Corporate Law: Structuring Your Business for Success
Corporate law governs how companies are formed, operated, and dissolved. The Corporations Act 2001 is the primary legislation in this area. One crucial aspect is understanding directors’ duties. Directors can face personal liability for breaches, with penalties reaching up to $1.11 million or three times the benefit derived from the contravention.
Recent trends show increased scrutiny on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) factors. The Australian Securities and Investment Commission (ASIC) has actively pursued cases of “greenwashing,” where companies make misleading claims about their environmental practices. In 2022, ASIC issued fines totalling $140,000 to several companies for such practices.
Consumer Protection: Safeguarding Rights and Obligations
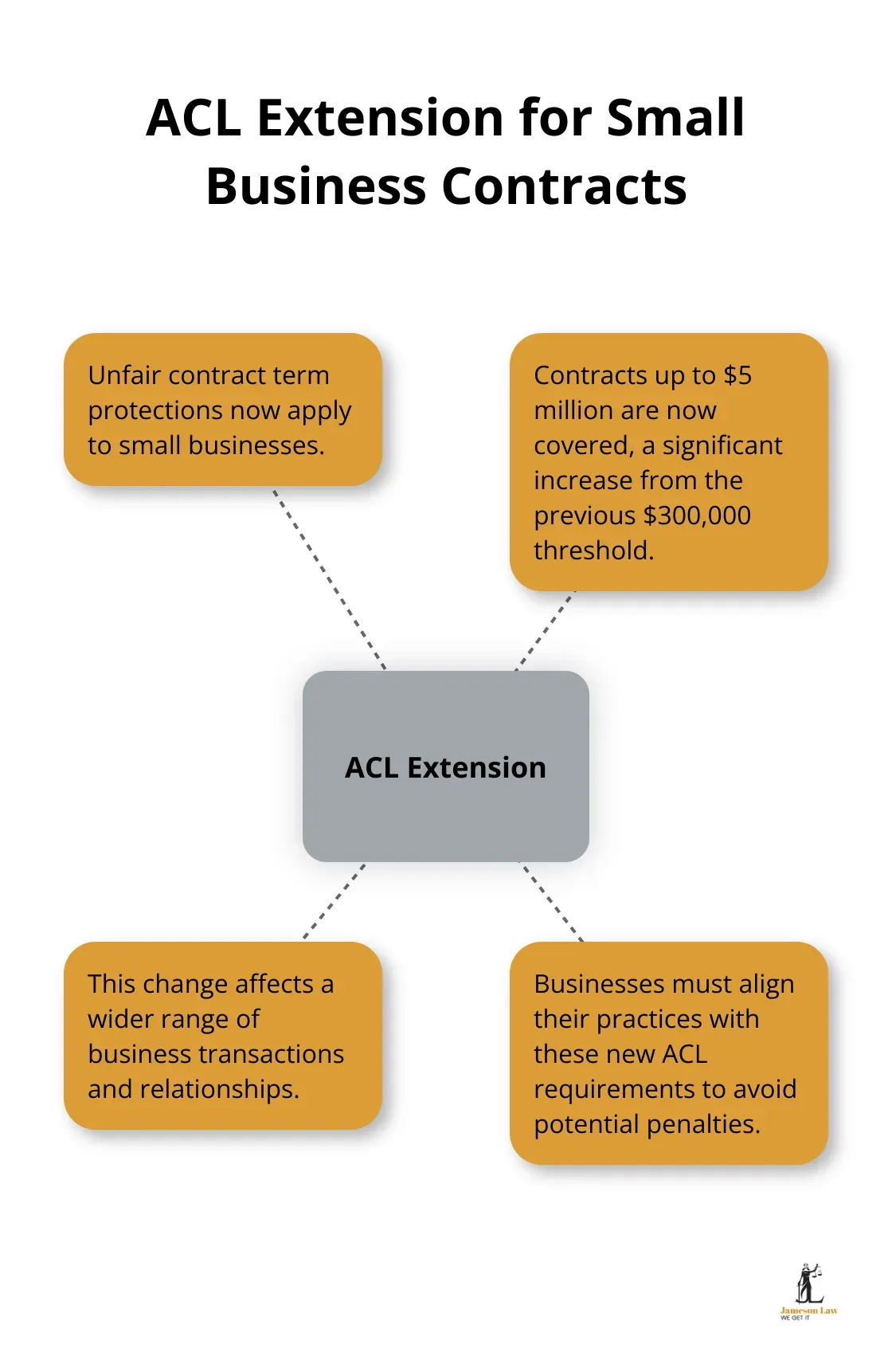
The Australian Consumer Law (ACL) sets out the rules for fair trading and consumer protection. One of the most significant recent developments is the extension of unfair contract term protections to small businesses. This change affects contracts up to $5 million, a substantial increase from the previous $300,000 threshold.
Businesses must align their practices with ACL requirements. The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) has been particularly active in enforcing these laws. In the 2021-2022 financial year, the ACCC secured over $200 million in penalties for breaches of consumer law.
Intellectual Property Law: Protecting Innovation and Creativity
Intellectual property (IP) law plays a vital role in safeguarding business innovations and creative assets. This area of law covers patents, trade marks, copyrights, and trade secrets. In Australia, the Intellectual Property Laws Amendment Act 2015 has strengthened the protection of IP rights.
Recent statistics from IP Australia show a significant increase in patent applications, with over 29,000 filed in 2022. This trend highlights the growing importance of IP protection in the Australian business landscape.
As we move forward to explore the important legislation in Australian Commercial Law, it’s clear that these key areas form the foundation of business operations and legal compliance in Australia.
Key Legislation Shaping Australian Commercial Law
Australian commercial law rests on several essential pieces of legislation that businesses must navigate to ensure compliance and protect their interests. These laws form the foundation of business operations and legal compliance in Australia.
The Corporations Act 2001: Cornerstone of Business Regulation
The Corporations Act 2001 establishes rules and regulations to ensure fair and transparent business practices, protect shareholders’ rights, and maintain the integrity of business operations in Australia. It covers a wide range of aspects, from company formation to winding up.
One of the Act’s most significant aspects focuses on director duties. Directors who breach their duties face severe penalties.
The Competition and Consumer Act 2010: Fair Business Practices
The Competition and Consumer Act 2010 aims to enhance the welfare of Australians by promoting competition among businesses, promoting fair trading by businesses, and protecting consumers. It includes the Australian Consumer Law (ACL) as a schedule, which we’ll explore in more detail.
This Act focuses on preventing anti-competitive behaviour. These figures demonstrate the serious consequences of breaching competition laws.
The Australian Consumer Law: Consumer and Small Business Protection
The ACL (part of the Competition and Consumer Act) sets out consumer rights and business obligations. Recent amendments have expanded its scope to protect small businesses from unfair contract terms.
This case highlights the importance of clear and honest communication with consumers.
The Personal Property Securities Act 2009: Asset Security
The Personal Property Securities Act 2009 (PPSA) establishes a national system for the registration and enforcement of security interests in personal property. This Act plays a critical role for businesses involved in lending or leasing.
Failing to register can lead to severe consequences.
These key pieces of legislation shape the commercial landscape and set the rules for fair and competitive business practices in Australia. As we move forward, we’ll examine how these laws impact dispute resolution in commercial matters, providing insights into the practical application of these regulations in business conflicts.
How Do Businesses Resolve Commercial Disputes in Australia?
Litigation in Australian Courts
Australian businesses often turn to litigation for resolving commercial disputes. The Federal Court of Australia and state Supreme Courts handle most significant commercial cases. In 2023, a total of 31,497 patent applications were filed, which is 2.4% below 2022 and 2.8% below the record high of 2021.

Litigation can be costly and time-consuming. The average duration of a commercial case in the Federal Court is approximately 8.7 months, with complex matters often taking much longer. Businesses should consider litigation as a final option, given its potential impact on resources and relationships.
Alternative Dispute Resolution
Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) methods have become more popular due to their cost-effectiveness and efficiency. The increasing use of Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) is one of the trends in commercial litigation.
Mediation proves particularly effective, with a high success rate in commercial disputes. This high success rate stems from the flexibility of the process and the ability of parties to maintain control over the outcome.
Arbitration is another popular ADR method, especially for international commercial disputes. The Australian Centre for International Commercial Arbitration (ACICA) handles arbitration cases. This trend reflects the growing preference for arbitration in cross-border commercial conflicts.
Role of Regulatory Bodies
Regulatory bodies play a significant role in dispute resolution and enforcement of commercial law in Australia. The Australian Securities and Investment Commission (ASIC) and the Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) are key players in this space.
ASIC, responsible for enforcing corporate law, initiates civil penalty proceedings, resulting in civil penalties. This demonstrates the regulator’s active role in maintaining corporate integrity and protecting stakeholders.
The ACCC, focusing on consumer protection and fair competition, secures penalties for breaches of the Competition and Consumer Act. These figures underscore the importance of regulatory compliance in avoiding costly disputes.
Businesses that proactively engage with regulatory bodies and seek early legal advice often achieve more favourable outcomes in commercial disputes. A well-prepared approach to dispute resolution, whether through litigation or ADR, can significantly impact the final result and preserve business relationships.
Final Thoughts
Australian commercial law encompasses various areas that shape business interactions. Key legislation, such as the Corporations Act 2001 and Competition and Consumer Act 2010, provides a framework for fair practices. Recent changes in unfair contract terms and increased focus on environmental factors highlight the dynamic nature of this field.
Understanding concise Australian commercial law principles enables businesses to make informed decisions and navigate disputes effectively. Companies must stay informed about regulatory changes to adapt and thrive in the Australian market. A proactive approach to commercial law can turn legal knowledge into a competitive advantage.
Jameson Law offers comprehensive commercial legal services tailored to your business needs. Our team can guide you through contract negotiations, corporate structuring, and dispute resolution (among other areas). We provide practical solutions to protect your interests and support your business growth in the complex landscape of Australian commercial law.
Ask ChatGPT













