The Contracts and Commercial Law Act 2017 has reshaped Australia’s commercial landscape. This landmark legislation consolidates multiple existing acts, simplifying the legal framework for businesses.
At Jameson Law, we’ve seen firsthand how this Act impacts our clients’ operations, from electronic transactions to goods and services regulations.
Our overview will explore key provisions, business impacts, and common legal issues arising from this significant reform.
Key Provisions of the Contracts and Commercial Law Act 2017
Consolidation of Existing Laws
While there were no major developments in the law of contract during 2017, there were a number of appellate judgments that delivered helpful summaries of existing principles. The consolidation of contract and commercial statutes aims to simplify the legal framework for businesses, potentially reducing compliance costs and time. This approach may create a more cohesive approach to commercial transactions.
Electronic Transactions and Contract Formation
The Act recognises electronic transactions as legally binding, a crucial step in the digital age. This provision has significant implications for Australian businesses, especially in the e-commerce sector. The Electronic Transactions Act 1999 (Cth), together with related state and territory legislation, forms the cornerstone of this legal recognition. This acknowledgment of electronic contracts supports the growing trend of digital transactions, enabling businesses to conduct them with confidence.
Rules for Sale of Goods and Services
The Act updates and clarifies rules for the sale of goods and services. It outlines specific implied warranties in consumer contracts. The Act states that every one of these contracts contains a number of obligations that sellers must honour. These provisions enhance consumer protection while providing clear guidelines for businesses to follow.
Carriage of Goods Regulations
The Act addresses the carriage of goods, updating regulations to reflect modern logistics practices. It clarifies the responsibilities of carriers and the rights of consignors and consignees. This update is particularly relevant given the importance of the freight and logistics industry to Australia’s economy.
Impact on Business Practices
These key provisions directly affect how businesses operate in Australia. Companies must ensure their digital contracts comply with the Act’s recognition of electronic transactions. Businesses involved in goods sales must be aware of the implied warranties to avoid potential legal issues.
The Act’s comprehensive nature requires businesses to review and update their existing contracts and procedures. Companies that adapt quickly to these changes (and seek expert legal advice when necessary) will be better positioned to thrive in Australia’s evolving commercial landscape. As we move forward, understanding the Act’s impact on businesses becomes increasingly important.
How the Contracts and Commercial Law Act 2017 Impacts Australian Businesses
The Contracts and Commercial Law Act 2017 has introduced significant changes for Australian businesses. These changes have wide-ranging implications across various sectors of the economy.
Simplified Legal Framework
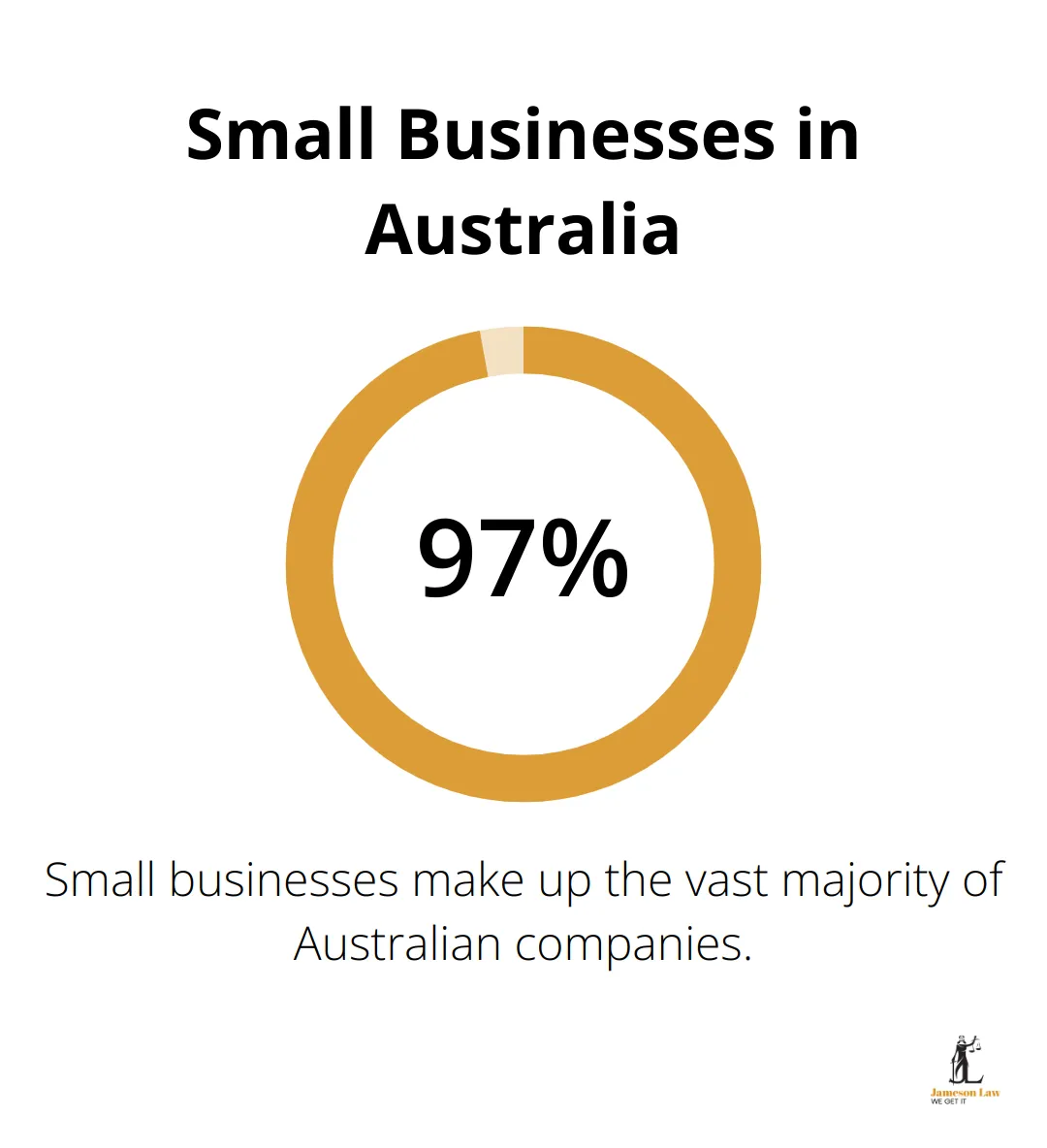
The Act’s consolidation of multiple existing laws has simplified the legal landscape for businesses. This streamlining reduces the complexity of navigating commercial transactions. Small businesses in Australia make up 97.2% of all businesses in Australia. For these smaller entities, a simplified legal framework can lead to substantial cost savings in legal compliance.
Stronger Consumer Protection
The Act bolsters consumer protection measures, which directly affects businesses. The implied warranties in consumer contracts now require businesses to increase transparency about their products and services. In 2022, the Federal Court ordered significant penalties against various businesses for breaches of the Australian Consumer Law. This highlights the need for businesses to thoroughly understand and comply with these enhanced protections.
Recognition of Digital Transactions
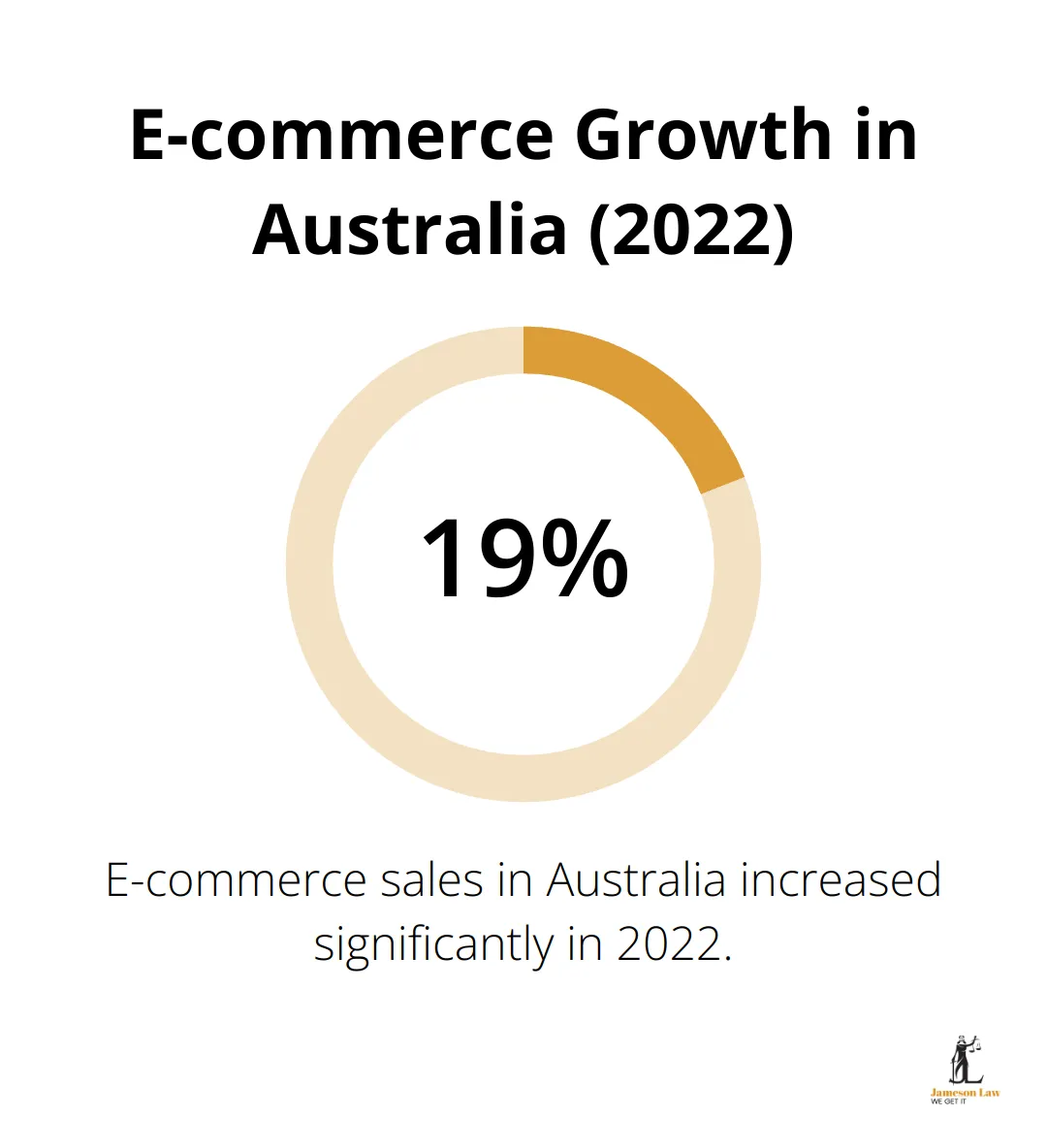
The Act’s recognition of electronic transactions as legally binding allows businesses to embrace digital platforms with confidence. This is particularly relevant given that e-commerce sales in Australia grew by 19.2% in 2022 (according to Australia Post’s eCommerce Industry Report). However, businesses must ensure their digital contracts comply with the Act’s provisions to avoid potential legal issues.
Changes in Liability and Risk Allocation
The Act introduces changes to liability and risk allocation in commercial transactions. These changes affect how businesses manage risk in their operations and contractual relationships. For example, the Act clarifies the responsibilities of carriers in the transportation of goods, which impacts businesses in the logistics and retail sectors.
Implications for Contract Drafting
The new legislation affects how businesses draft and interpret contracts. Companies need to review and update their existing contracts to ensure compliance with the Act’s provisions. This process may require legal expertise to navigate the nuances of the new legislation (Jameson Law offers comprehensive commercial law services to assist businesses in this area).
The Act’s impact on Australian businesses is substantial and multifaceted. It offers opportunities for streamlined operations and digital growth, while also demanding increased vigilance in consumer protection and contract compliance. As businesses adapt to these changes, they may encounter various legal challenges. The next section will explore some common legal issues and case studies arising from the implementation of the Contracts and Commercial Law Act 2017.
Real-World Legal Challenges Under the New Act
Contract Formation Disputes in the Digital Age
The Contracts and Commercial Law Act 2017 recognises electronic transactions, which has led to new types of contract formation disputes. A recent case involved an online retailer facing legal action when a customer claimed they never agreed to certain terms during a digital transaction. The court ruled in favour of the retailer, citing the clear presentation of terms on the website and the customer’s affirmative action in clicking ‘agree’. This case emphasises the need for clear, accessible terms in digital contracts.
Consumer Rights Violations
Consumer rights violations have become a central issue under the new Act. The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) will introduce a new priority in 2025-26 to address misleading surcharging practices and other add-on costs. In one notable case, a major appliance manufacturer received a $3.5 million fine for false claims about product performance. This case highlights the importance of accurate product descriptions and marketing materials for businesses.
Warranty Breaches and Their Consequences
The Act’s emphasis on implied warranties has increased scrutiny of goods and services. A landmark case in 2023 resulted in a car manufacturer paying damages for breaching warranties related to vehicle emissions. This case serves as a warning about the financial and reputational risks associated with warranty breaches. Businesses must ensure their products and services meet all stated and implied warranties to avoid similar issues.
Carriage of Goods Disputes
The Act’s updated regulations on the carriage of goods have led to new legal challenges in the logistics sector. A recent dispute between a major retailer and a freight company centred on liability for damaged goods during transit. The court’s interpretation of the Act’s provisions on risk allocation during transportation set a precedent for future cases in this area.
Electronic Evidence in Contract Disputes
With the increased recognition of electronic transactions, courts now face new challenges in evaluating electronic evidence in contract disputes. A recent case involved the admissibility of blockchain-based smart contracts as evidence. The court’s decision to accept this evidence as valid (under certain conditions) marks a significant shift in how digital contracts are treated in legal proceedings.

Final Thoughts
The Contracts and Commercial Law Act 2017 has transformed Australia’s commercial landscape. This legislation streamlines legal frameworks, enhances consumer protections, and recognizes digital transactions. Companies must adapt their practices, from contract drafting to risk management, to align with the updated regulations.
Recent legal cases highlight the importance of compliance with the Act. From disputes over digital contract formation to significant fines for consumer rights violations, these examples underscore the need for businesses to stay informed. Companies should review their existing business processes to ensure they meet the Act’s requirements for electronic transactions, implied warranties, and liability allocation.
We at Jameson Law specialize in navigating the complexities of commercial law. Our team helps businesses understand their contractual obligations and mitigate legal risks under the Contracts and Commercial Law Act 2017. We provide tailored support to help companies thrive in this evolving commercial environment.













