The Industrial Relations Commission of New South Wales plays a vital role in shaping the state’s employment landscape. This independent tribunal handles a wide range of workplace disputes and sets standards for fair employment practices.
At Jameson Law, we understand the importance of navigating the complex world of industrial relations. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the history, structure, and key functions of the Commission, providing valuable insights for employers and employees alike.
What is the Industrial Relations Commission of NSW?
Establishment and Historical Context
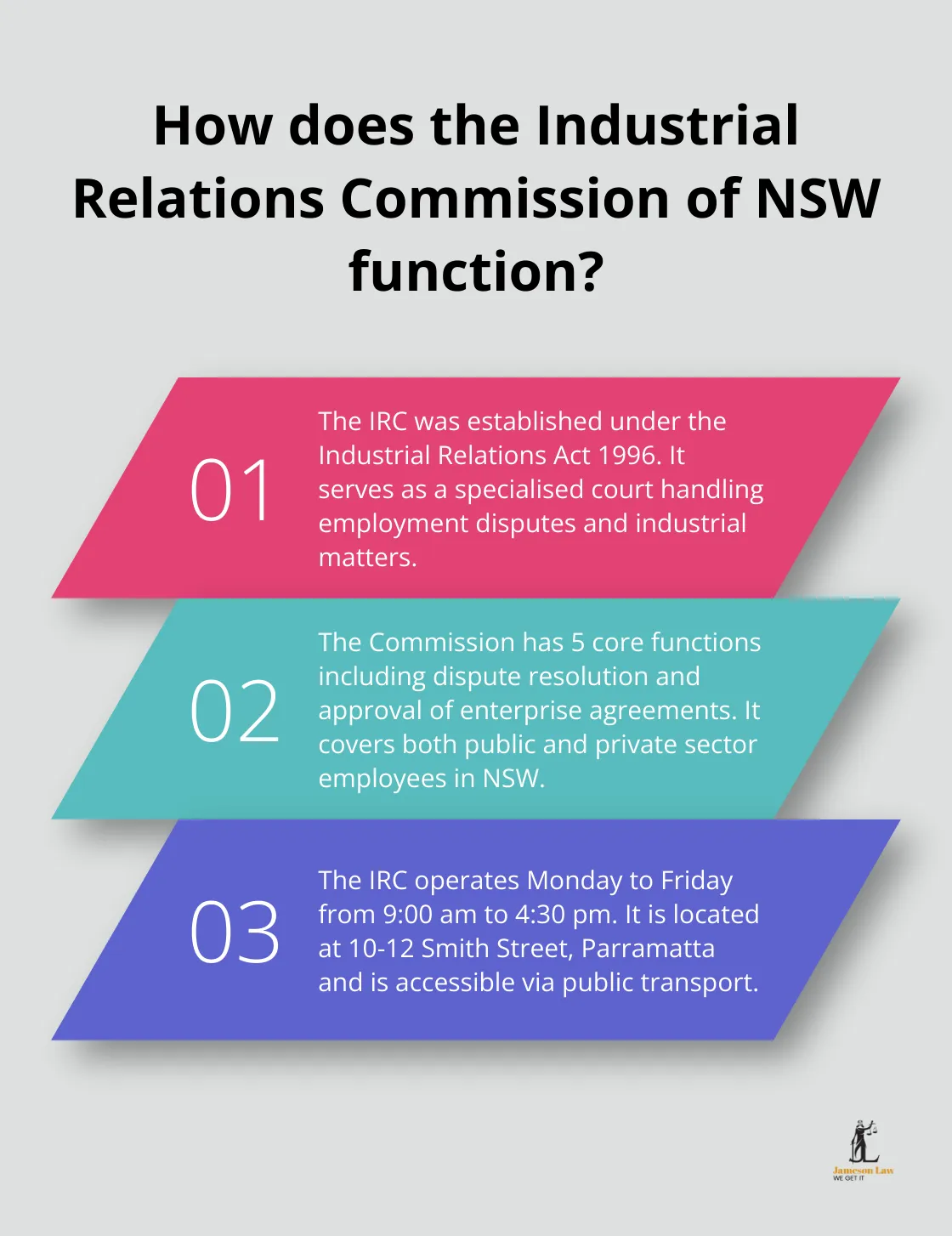
The Industrial Relations Commission of New South Wales (IRC) was established under the Industrial Relations Act 1996. It serves as a crucial institution for maintaining fair employment practices in the state, with conciliation and arbitral functions.
Core Functions and Responsibilities
The IRC serves as a specialised court handling disputes related to employment, workplace agreements, and industrial matters. Its primary functions include:
- Resolution of industrial disputes through conciliation and arbitration
- Approval of enterprise agreements
- Issuance and interpretation of industrial awards
- Management of unfair dismissal claims
- Determination of minimum wages and working conditions
The Commission’s role extends beyond dispute resolution; it actively shapes the industrial landscape by establishing standards that foster fair and productive workplaces across NSW.
Jurisdiction and Legal Authority
The IRC wields substantial power within the state’s industrial relations framework. Its authority encompasses:
- Making binding decisions on industrial matters
- Issuing orders to halt industrial action
- Conducting inquiries into workplace issues
- Imposing penalties for breaches of industrial laws
The IRC’s jurisdiction covers both public and private sector employees in NSW (excluding those under federal awards or agreements).
Impact on Employers and Employees
For employers, a thorough understanding of the IRC’s role is essential. It’s not merely about compliance; it’s about creating an equitable and productive workplace. Employers who actively engage with the IRC’s guidelines often find themselves better prepared to address workplace issues before they escalate.
Employees reap numerous benefits from the IRC’s oversight. The Commission ensures fair wages, protection from unfair dismissal, and provides a platform to address workplace grievances.
Accessibility and Operations
The IRC maintains a registry that operates Monday to Friday (9:00 am to 4:30 pm) for inquiries and claims submissions. Located at 10-12 Smith Street, Parramatta, the Commission offers easy access via public transport.
Those considering lodging a claim or seeking information should note that initial consultations with experienced legal professionals (such as those at Jameson Law) can significantly enhance their understanding and approach to the IRC process.
Recent Trends and Future Outlook
The New South Wales (NSW) Government has recently flagged a major shake-up to the state’s workers’ compensation and anti-bullying systems. As workplace dynamics continue to evolve, the IRC’s ability to provide fair, timely resolutions will remain central to maintaining harmonious industrial relations across NSW. The next section will explore the structure and operations of the Commission in greater detail, shedding light on how it fulfils its vital role in the state’s employment landscape.
How Does the Industrial Relations Commission Operate?
Commission Composition
The Industrial Relations Commission of New South Wales (IRC) consists of a President, Vice Presidents, Deputy Presidents, and Commissioners. These members bring diverse expertise in industrial relations, law, and economics. The IRC operates through various divisions, including the Unfair Dismissal Division, the Dispute Resolution Division, and the Award Review Division. This structure allows for efficient handling of specific case types.
Types of Proceedings
The IRC conducts several types of proceedings to address workplace disputes:
- Conciliation conferences: Informal meetings to resolve disputes through mutual agreement.
- Arbitration hearings: Formal proceedings where the Commission makes binding decisions after hearing evidence.
- Award variation hearings: Sessions to review and update industrial awards.
- Unfair dismissal hearings: Proceedings to determine the validity of termination claims.

In 2024, unfair dismissal applications made up 37% of the Commission’s caseload, together with general protections involving dismissal.
Decision-Making Process
The IRC’s decision-making process is rigorous and transparent. Commissioners consider evidence, relevant laws, and precedents before reaching a verdict. The Commission publishes decisions on its website, which promotes accountability and provides guidance for future cases.
Appeals Mechanism
Parties dissatisfied with an IRC decision have the right to appeal. A Full Bench of the Commission (consisting of three or more members) typically hears appeals. In some cases, appeals may proceed to the NSW Supreme Court on questions of law.
The appeal process is not a mere formality. Appeals from decisions of the Full Bench of the Industrial Relations Commission can result in reversals of previous decisions, underscoring the importance of a robust appeals mechanism.
Impact on Employers and Employees
For employers, a thorough understanding of the IRC’s role is essential. It’s not merely about compliance; it’s about creating an equitable and productive workplace. Employers who actively engage with the IRC’s guidelines often find themselves better prepared to address workplace issues before they escalate.
Employees benefit from the IRC’s oversight in numerous ways. The Commission ensures fair wages, protection from unfair dismissal, and provides a platform to address workplace grievances.
The IRC’s structure and operations play a vital role in shaping the industrial relations landscape of NSW. As we move forward, it’s important to examine the key areas where the Commission focuses its efforts and how these impact both employers and employees across the state.
Key Focus Areas of the Industrial Relations Commission
Workplace Dispute Resolution
The Industrial Relations Commission of New South Wales (IRC) resolves industrial disputes efficiently. The Commission is established under the Industrial Relations Act 1996 with conciliation and arbitral functions. This process involves neutral third-party facilitation, which encourages parties to reach mutually agreeable solutions.

Employers and employees who face disputes should consider early engagement with the IRC’s conciliation services. This approach can lead to faster resolutions and reduced costs.
Unfair Dismissal Claims
Unfair dismissal claims constitute a substantial part of the IRC’s workload. The IRC assesses whether a dismissal was harsh, unjust, or unreasonable. It considers factors such as valid reason, notification, and opportunity to respond.
Employers must maintain proper documentation and follow fair procedures to defend against unfair dismissal claims. Employees need to understand the lodgement deadline and eligibility criteria before pursuing a claim.
Award Interpretation and Enforcement
The IRC interprets and enforces industrial awards. These legally binding documents set minimum employment conditions for specific industries or occupations.
Employers must stay informed about relevant award changes to ensure compliance. The IRC’s website provides up-to-date information on award variations and interpretations. Employees can use this resource to understand their entitlements and rights under applicable awards.
Work Health and Safety Oversight
While SafeWork NSW holds primary responsibility for work health and safety (WHS), the IRC contributes significantly to this area. The Commission hears appeals against improvement notices issued by SafeWork NSW inspectors and resolves disputes related to WHS issues.
Employers should prioritise WHS compliance to avoid potential disputes and legal consequences.
Impact on Employers and Employees
The IRC’s focus on these key areas demonstrates its commitment to maintain fair and safe workplaces across NSW. Employers who understand and engage with the Commission’s processes can navigate the complex industrial relations landscape more effectively. For employees, the IRC provides a platform to address workplace grievances and ensure fair treatment.
Final Thoughts
The Industrial Relations Commission of New South Wales maintains fair employment practices and workplace relations in the state. It resolves disputes, interprets awards, and sets standards for workplace conduct, shaping the broader industrial landscape. Recent developments in NSW industrial relations law highlight the Commission’s adaptability, with new protections for employees and expanded powers to address gig economy issues.

The Commission will address emerging challenges as technology reshapes employment relationships. Employers and employees must stay informed about these developments to navigate the changing landscape effectively. The Commission’s website offers resources, including practice notes, forms, and procedural guides.
Expert assistance often proves necessary to navigate workplace law complexities. Jameson Law provides comprehensive legal support in industrial relations and other areas of law. We help both employers and employees understand their rights and obligations under the Industrial Relations Commission’s purview.













