Section 75(2) of the Family Law Act is a cornerstone of property settlements in Australian family law. It outlines crucial factors that courts must consider when dividing assets after a relationship breakdown.
At Jameson Law, we understand the complexities of this provision and its significant impact on financial outcomes for separating couples.
This blog post will break down the key elements of Section 75(2) and explain how they influence property division decisions in family law cases.
What is Section 75(2) of the Family Law Act?
Definition and Purpose
Section 75(2) of the Family Law Act 1975 stands as a cornerstone of Australian family law. It outlines specific factors that courts must consider when making property settlements after a relationship breakdown. The primary purpose of this section is to ensure fair and just division of assets, recognising that each case requires a unique approach.
Key Factors Considered
Under Section 75(2), courts must take into account several factors:
- Age and health of both parties
- Income, property, and financial resources
- Caring responsibilities for children
- Ability to earn an income
- Marriage duration and its impact on earning capacity
- Need to protect a party who wishes to continue parenting
These factors help courts assess both current and future needs of the parties involved, ensuring long-term fairness in property settlements.
Impact on Property Settlements
Section 75(2) significantly shapes property settlements by allowing courts to adjust asset division based on individual circumstances. For example, a party with lower earning capacity due to their role as primary caregiver might receive a larger portion of the property pool to account for future needs.
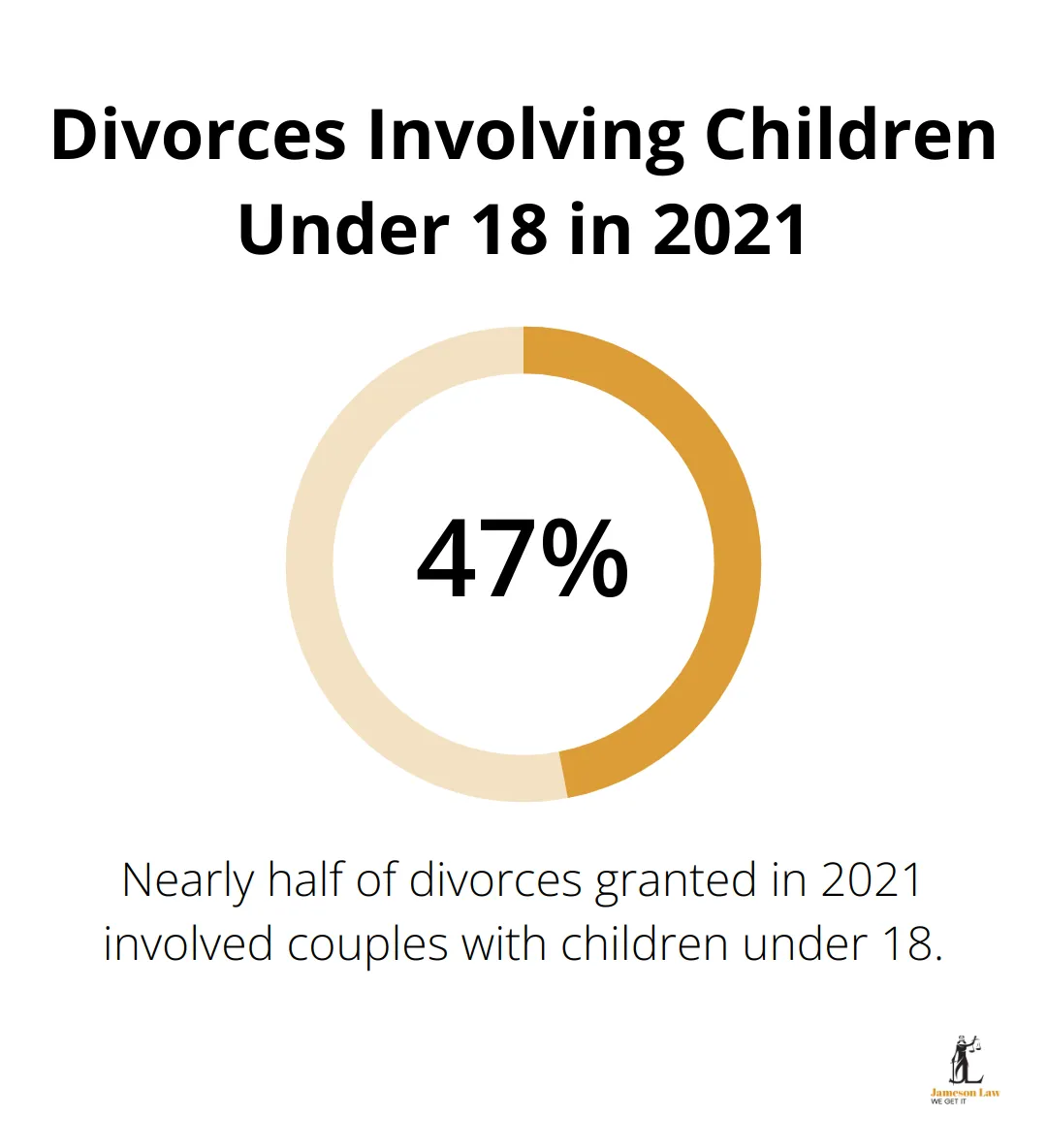
Nearly half (47.8%) of the divorces granted in 2021 were for couples with children under the age of 18. This statistic underscores the importance of Section 75(2) in protecting parents who may have sacrificed career opportunities for family responsibilities.
Real-World Application
In practice, Section 75(2) factors can dramatically influence settlement outcomes. For instance, a person with chronic health issues might receive a larger share of assets due to reduced work capacity and higher ongoing medical expenses.
Importance of Legal Advice
Understanding Section 75(2) is essential for anyone facing separation or divorce. It’s not simply about equal division; it’s about creating a fair and sustainable financial future for both parties. Expert legal advice can ensure that your rights and needs are properly considered under this section.
As we move forward, let’s examine each factor of Section 75(2) in detail to gain a comprehensive understanding of how courts apply these considerations in property settlements.
What Factors Shape Property Settlements?
Age and Health Considerations
Section 75(2) of the Family Law Act outlines several key factors that courts consider when determining property settlements. The age and health of both parties play a significant role in these decisions. This section of the Family Law Act relates to adjusting a property settlement based on the contributions of the parties.
Financial Resources and Earning Capacity
Courts closely examine each party’s income, property, and financial resources. This includes not just current assets, but also future earning potential. The current and potential future earning capacity of each of the parties must also be considered.
Parental Responsibilities and Child Support
Caring for children is a major factor in property settlements. The primary caregiver often receives a larger share of assets to reflect their ongoing responsibilities and potential impact on earning capacity.
Child custody arrangements contribute to a longer duration in property settlement cases by 20-30%.

Standard of Living
The court considers the standard of living enjoyed by the couple during their relationship. This factor helps ensure that neither party experiences a drastic decline in their quality of life post-separation (where possible).
Contributions to the Relationship
Both financial and non-financial contributions to the relationship are considered. This includes direct financial contributions, as well as indirect contributions such as homemaking and child-rearing.
The application of these factors under Section 75(2) is complex and requires expert legal guidance. In the next section, we’ll explore how courts apply these factors in real-world scenarios, and the impact they can have on property settlement outcomes.
How Courts Apply Section 75(2)
Balancing Multiple Factors
Courts don’t follow a strict formula when applying Section 75(2) of the Family Law Act. They weigh each factor carefully, considering how they interact and impact the overall financial picture for both parties. A spouse with limited earning capacity due to health issues might receive a larger share of the property pool to account for ongoing medical expenses and reduced ability to work.
Parental Responsibilities and Asset Division
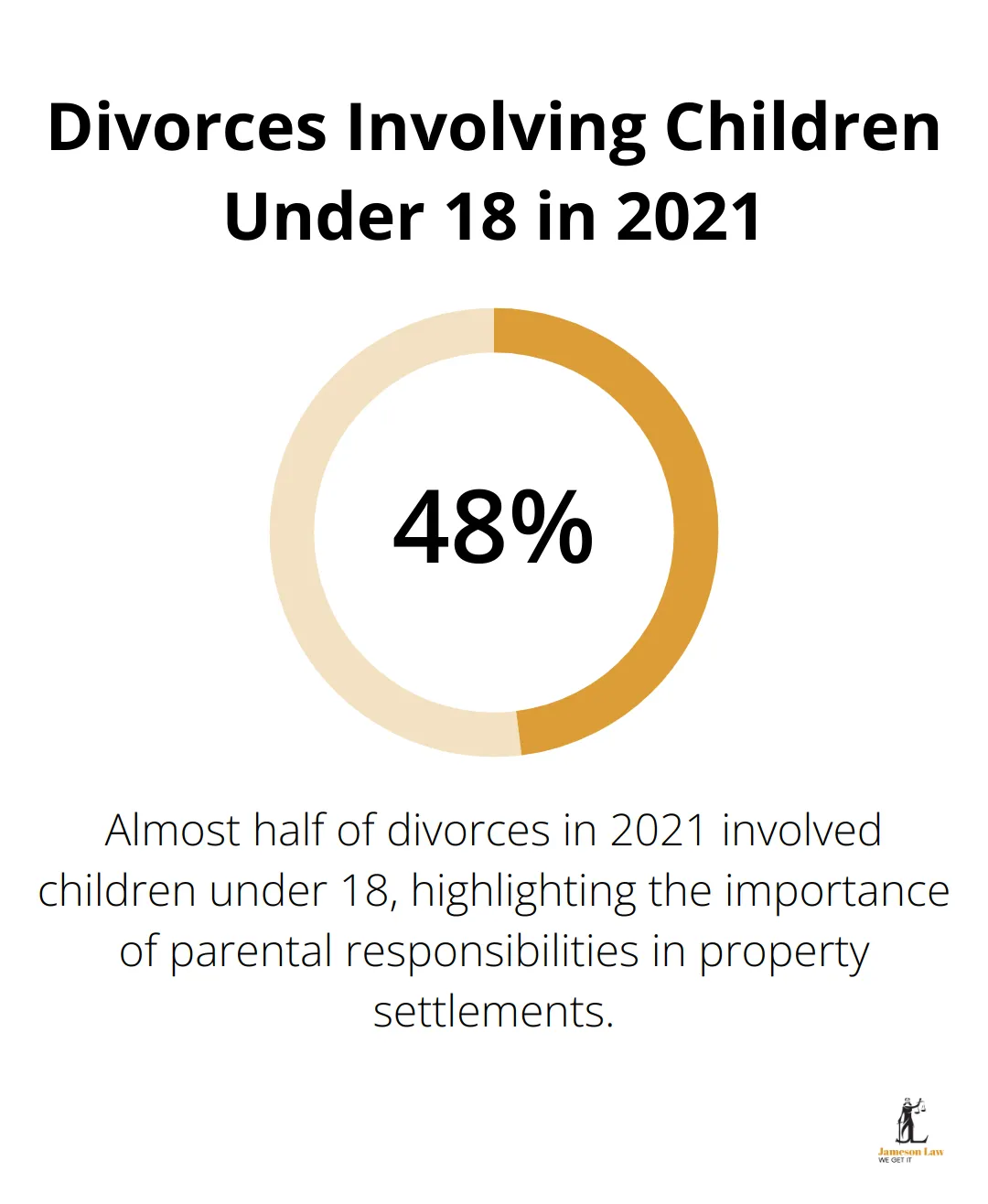
Parental responsibilities significantly influence property settlements. In 2021, 48% of divorces involved children under 18. This statistic underscores the importance courts place on ensuring the primary caregiver has sufficient resources to maintain the children’s standard of living post-separation.
Long-term Financial Security Considerations
Courts look beyond immediate asset division and consider long-term financial security. A spouse who took career breaks to raise children might receive a larger portion of superannuation to offset reduced retirement savings. Women’s superannuation balances are typically more than 40% less than men’s, which highlights the need for this consideration.
Real-World Case Examples
Health and Caregiving Factors
In one notable case, the court awarded a wife 70% of the asset pool due to her role as primary caregiver, limited earning capacity, and ongoing health issues. This decision reflected the court’s application of multiple Section 75(2) factors to ensure her future financial stability.
Medical Expenses and Asset Division
Another case saw a 60-40 split in favour of the husband, who had significant ongoing medical expenses due to a chronic condition. The court determined this division would best meet his future needs while still providing for the wife’s financial security.
Dispelling Common Misconceptions
Many people incorrectly believe that property settlements always result in a 50-50 split. However, Section 75(2) allows for adjustments based on individual circumstances. Another misconception is that financial contributions are the only factor considered. In reality, non-financial contributions (such as homemaking and child-rearing) carry significant weight in the court’s deliberations.
Final Thoughts
Section 75(2) of the Family Law Act shapes fair property settlements in Australia. Courts consider factors beyond financial contributions, including age, health, earning capacity, and parental responsibilities. This provision aims to create settlements that provide long-term financial stability for both parties.
The complexity of Section 75(2) highlights the need for expert legal advice when navigating property settlements. Each case requires a unique approach, and the application of these factors can significantly impact the final outcome. Professional guidance helps you understand how the court might apply Section 75(2) of the Family Law Act to your specific situation.
Jameson Law specializes in guiding clients through family law matters, including property settlements. Our team of experienced lawyers understands the nuances of Section 75(2) and how it influences court decisions. We offer tailored legal strategies and clear communication to protect your interests in complex family law matters.













