Corporate commercial law forms the backbone of modern business operations. It encompasses a wide range of legal concepts that are essential for companies to navigate successfully.
At Jameson Law, we understand the complexities of this field and its impact on businesses of all sizes. This blog post will explore key concepts in corporate commercial law, providing insights into corporate structures, commercial contracts, and mergers and acquisitions.
How Corporate Structures Shape Business Success
Choosing the Right Business Entity
Corporate structures and governance form the foundation of any successful business in Australia. These elements define how a company operates, makes decisions, and protects its stakeholders.
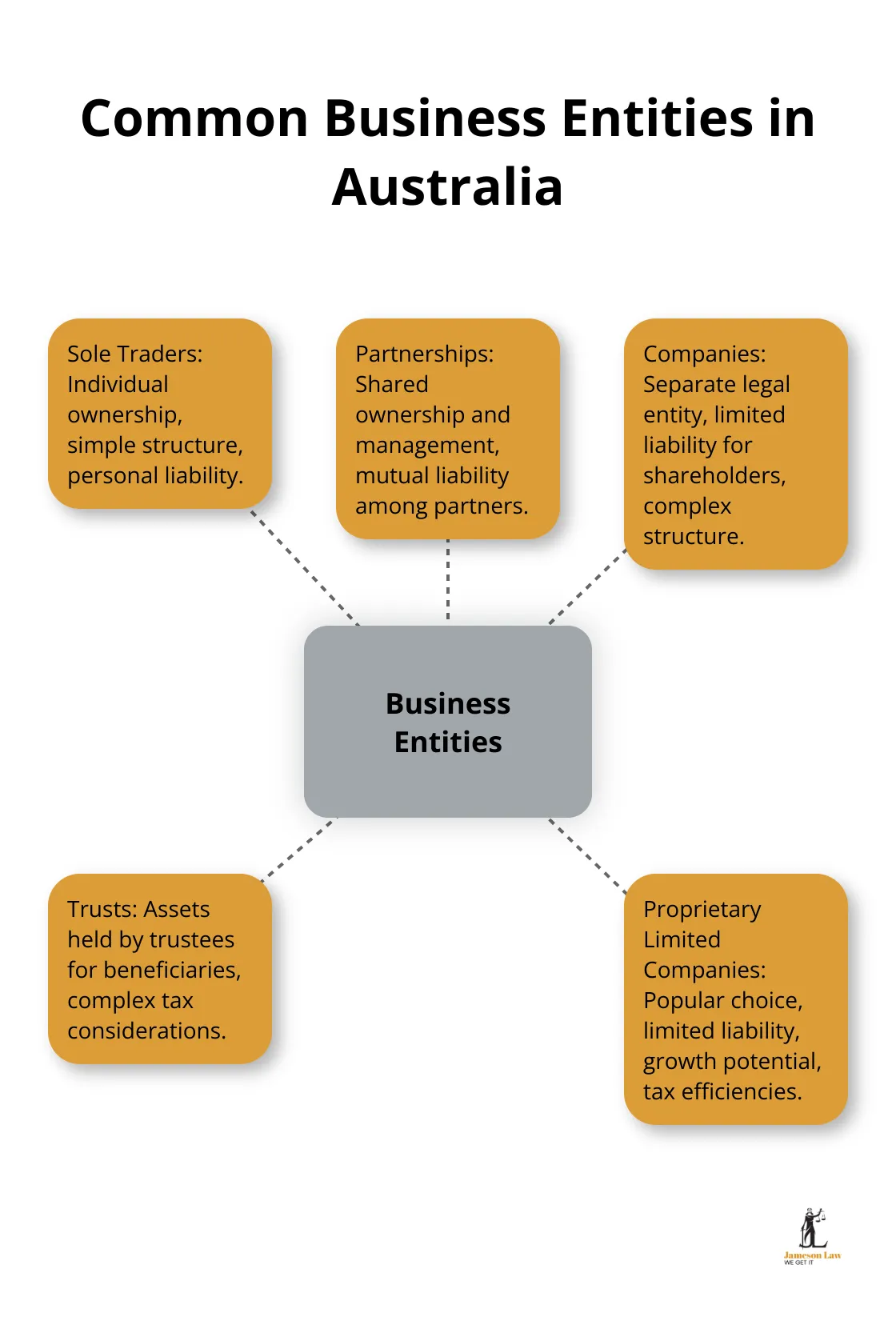
In Australia, businesses can choose from several entity types, each with its own legal and tax implications. The most common are sole traders, partnerships, companies, and trusts. Proprietary limited companies are popular due to their limited liability protection, growth potential, and certain tax efficiencies.
The Australian Bureau of Statistics reports that as of June 2024, there are 2,662,998 actively trading businesses in Australia, with 999,161 of these businesses being employing. This diverse landscape underscores the importance of selecting the right structure for your business goals.
The Weight of Directors’ Responsibilities
Directors in Australian companies carry significant legal duties. These include:
- Acting in good faith
- Avoiding conflicts of interest
- Preventing insolvent trading
The consequences of breaching these duties can be severe. The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) plays a crucial role in enforcing these responsibilities.
Protecting Shareholder Interests
Shareholders are the lifeblood of many companies, and their rights are protected under the Corporations Act 2001. These rights include:
- Voting on major company decisions
- Receiving dividends
- Accessing company information
A key aspect of shareholder protection is the Annual General Meeting (AGM). Public companies must hold their AGM within five months after the end of their financial year, ensuring transparency and accountability.
Practical Steps for Robust Governance
To maintain strong corporate governance, we recommend implementing these practical steps:
- Establish a clear governance structure with defined roles and responsibilities.
- Conduct regular board meetings (ideally quarterly) to review performance and compliance.
- Implement an annual compliance calendar to track important corporate obligations.
- Provide ongoing training for directors on their legal responsibilities and emerging corporate governance trends.
These areas create a solid foundation for growth and mitigate potential legal risks. Effective corporate structures and governance aren’t just about compliance – they create a framework for sustainable business success.
As we move from the internal workings of a company to its external relationships, let’s explore the world of commercial contracts and agreements. These legal instruments form the basis of business interactions and can significantly impact a company’s success or failure.
Mastering Commercial Contracts for Business Success
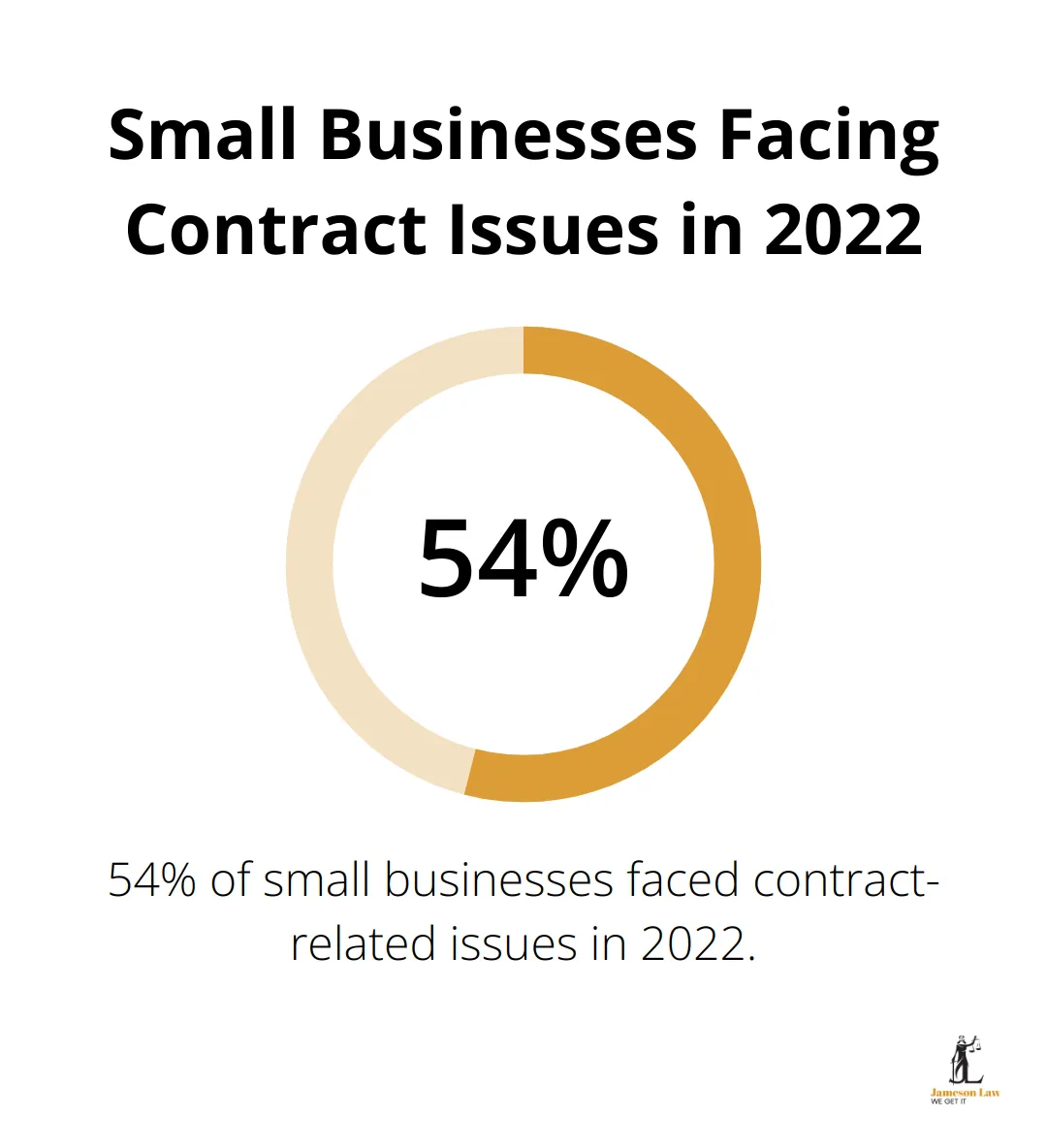
Commercial contracts form the foundation of business relationships. They define obligations, allocate risks, and provide a roadmap for successful partnerships. In Australia, 54% of small businesses faced contract-related issues in 2022. This statistic highlights the critical need for businesses to understand and effectively manage their commercial agreements.
The Building Blocks of Valid Contracts
For a contract to be legally binding in Australia, it must contain several key elements:
- Offer
- Acceptance
- Consideration
- Intention to create legal relations
- Capacity to contract
While these may seem straightforward, the details can be complex. The case of Pipikos v Trayans (2019) in the High Court of Australia demonstrated how uncertain terms can render a contract unenforceable, even when parties believe they have reached an agreement.
To avoid such pitfalls, businesses should clearly define all terms and conditions in writing. This includes specifying the goods or services to be provided, payment terms, delivery timelines, and dispute resolution mechanisms. A solid foundation for business relationships minimizes the risk of costly misunderstandings.
Navigating Common Commercial Agreements
In the Australian business landscape, certain types of contracts are more prevalent than others:
- Supply agreements
- Distribution agreements
- Franchise agreements
- Lease agreements
- Employment contracts
Each of these agreements comes with its own set of legal considerations. For example, franchise agreements must comply with the Franchising Code of Conduct (a mandatory industry code under the Competition and Consumer Act 2010). Failure to adhere to this code can result in significant penalties.
Employment contracts must align with the Fair Work Act 2009, which sets out minimum employment standards. In the 2021-22 financial year, the Fair Work Ombudsman recovered over $123 million in unpaid wages, emphasizing the importance of getting these contracts right.
Crafting Effective Agreements
When drafting and negotiating commercial contracts, attention to detail is paramount. Here are some practical tips to enhance contract management:
- Use clear, unambiguous language. Avoid jargon and complex legal terms that may confuse non-lawyers.
- Include a well-defined scope of work or services. This prevents scope creep and ensures all parties are on the same page.
- Clearly outline payment terms (including amounts, timelines, and methods of payment).
- Incorporate appropriate risk allocation clauses, such as indemnities and limitations of liability.
- Include dispute resolution clauses that specify how conflicts will be handled, potentially saving time and money in the long run.
- Regularly review and update contracts to ensure they remain relevant and compliant with current laws.
These strategies create robust agreements that protect interests and foster positive business relationships. While templates can be a useful starting point, every business situation is unique. Tailoring contracts to specific needs and having them reviewed by a legal professional provides an extra layer of protection.
Embracing Digital Transformation in Contracts
The rise of digital transformation has led to increased use of electronic signatures and smart contracts. While these technologies offer efficiency, they also bring new legal considerations. The Electronic Transactions Act and similar laws make electronic signatures generally legal and binding for business agreements in Australia. Businesses should familiarise themselves with this legislation and seek legal advice to ensure their digital contracts are enforceable.
As the business world continues to evolve, so too does the landscape of mergers and acquisitions. These complex transactions require a deep understanding of both corporate and commercial law principles. Let’s explore the key aspects of M&A deals and their impact on Australian businesses.
Navigating M&A Deals in Australia
Types of M&A Transactions
M&A deals reshape industries and create new market dynamics. In 2022, Australia witnessed M&A deals with aggregate transaction value of $45.4 billion, a third of the unprecedented $130.6 billion deal value announced in 2021. This level of activity highlights the importance of understanding M&A transactions.
M&A deals come in various forms, each with unique legal considerations:
- Asset acquisitions: Involve purchasing specific assets of a target company.
- Share acquisitions: Entail buying the shares of the target company.
- Mergers: Combine two separate entities into a single new company.
The choice of transaction type significantly impacts tax implications, liability transfer, and regulatory requirements. Asset acquisitions often allow buyers to select desirable assets and avoid certain liabilities, but they can be more complex from a tax perspective.
The Critical Role of Due Diligence
Legal due diligence forms a cornerstone of successful M&A transactions. This process involves a comprehensive review of the target company’s legal, financial, and operational aspects. Key areas of focus include:
- Corporate structure and governance
- Material contracts and commitments
- Intellectual property rights
- Employment matters
- Regulatory compliance
- Pending or potential litigation

Due diligence ensures the acquirer is as fully informed as possible about the possible risks of an acquisition prior to completing the transaction. It also informs the negotiation process and helps structure the transaction to mitigate risks.
The 2011 acquisition of Centro Properties Group by Blackstone (valued at $9.4 billion) faced significant challenges due to undisclosed liabilities discovered during the due diligence process, leading to a restructuring of the transaction terms.
Navigating Regulatory Hurdles
M&A transactions in Australia must comply with various regulatory requirements:
- The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) assesses the competitive impact of proposed mergers. Transactions that may substantially lessen competition in a market face scrutiny and potential opposition.
- The Foreign Investment Review Board (FIRB) regulates foreign investment in Australian businesses. The Australian Treasurer is responsible for decisions under the FATA and is advised by the FIRB. Certain transactions require FIRB approval, with thresholds and requirements varying based on the industry sector and the nature of the foreign investor.
- The Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) oversees compliance with the Corporations Act 2001, which governs many aspects of M&A transactions (including disclosure requirements and shareholder approvals).
These regulatory requirements demand careful planning and expert legal guidance. Failure to comply can result in significant penalties and even transaction termination. In 2020, the Federal Court of Australia imposed a $1 million penalty on Cryosite Limited for engaging in cartel conduct during its asset sale to Cell Care Australia Pty Ltd.
Legal Expertise in M&A Transactions
M&A transactions require a deep understanding of corporate and commercial law. From selecting the right transaction structure to conducting thorough due diligence and ensuring regulatory compliance, each step demands careful consideration and expert guidance.
As the Australian M&A landscape continues to evolve, businesses must stay informed about legal developments and seek professional advice. Jameson Law offers comprehensive legal services for M&A transactions, providing tailored support to navigate these complex deals successfully.
Final Thoughts
Corporate commercial law forms the foundation of successful business operations in Australia. Understanding key concepts in corporate structures, commercial contracts, and mergers and acquisitions helps companies navigate the complex business landscape. The ever-evolving nature of corporate commercial law demands ongoing attention and expertise from businesses facing numerous legal challenges.
Professional legal advice proves essential for businesses to avoid costly mistakes, mitigate risks, and capitalise on opportunities. Jameson Law offers comprehensive legal services tailored to the unique needs of Australian businesses. Our team brings experience to address a wide range of corporate commercial law matters.
A proactive legal strategy provides invaluable benefits in today’s fast-paced business environment. Companies can save time, money, and resources by anticipating legal challenges and addressing them early. This approach also positions businesses to seize growth opportunities with confidence, knowing they have a solid legal foundation.













